Debugging Evals
Quick Summary
Confident AI uses "tracing" to help debug unsatisfactory evaluation results. Tracing in the context of evaluating LLM applications provides a quick and easy way for you to identify why certain test cases are failing on specific metrics.
From chunking to embedding, retrieval to generation, tracing allows you to debug your LLM application pipeline at a component level.
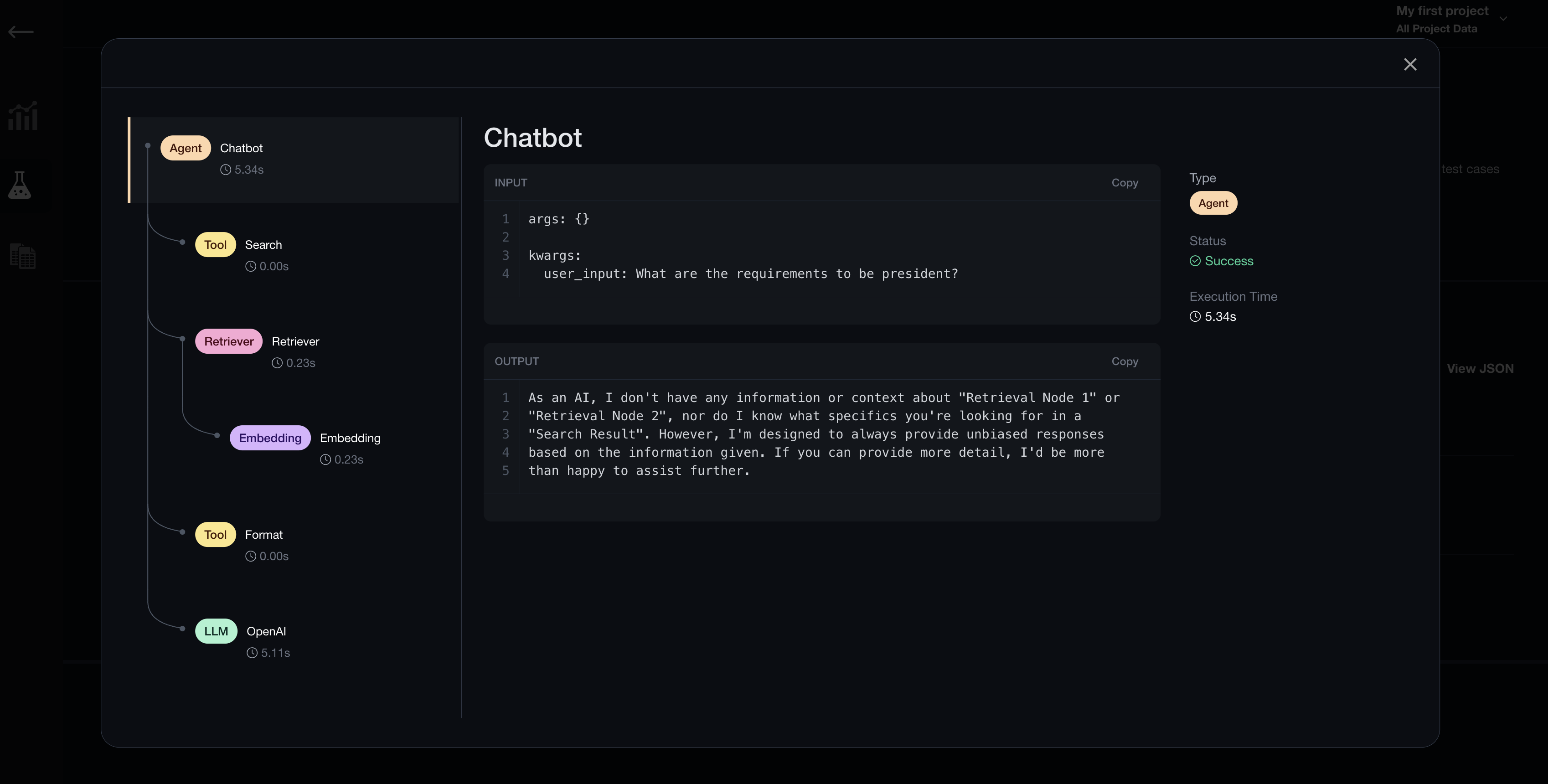
Trace Decorator
The @trace decorator is a decorator offered by deepeval for you to easily track the input and outputs of different components in your retrieval pipeline that make up your LLM application. The @trace decorator accepts three arguments: type, name, and model.
Trace Type
The type parameter is an easy way for you to classify components in your pipeline and can either be of type TraceType, or str (for custom types). Here are all the TraceType deepeval offers:
TraceType.LLMTraceType.RetriverTraceType.EmbeddingTraceType.ToolTraceType.AgentTraceType.Chain
from deepeval.tracing import TraceType
@trace(type=TraceType.LLM, ...)
def llm(messages):
...
Trace Name
The name parameter is optional and defaults to the function/method name if left blank. It has no functionality other than providing you a way to distinguish between different functions/methods decorated with the same trace type.
from deepeval.tracing import TraceType
@trace(type=TraceType.LLM, name="OpenAI", ...)
def llm(messages):
...
Trace Model
The model parameter is only required for when the trace type is either TraceType.LLM or TraceType.EMBEDDING. It expects a string which should be the name of the model you're currently using.
from deepeval.tracing import TraceType
@trace(type=TraceType.LLM, name="OpenAI", model="gpt-4")
def llm(messages):
...
Setup Tracing
Import the @trace decorator from deepeval.tracing and apply it to functions/methods that make up your LLM pipeline. Here's an implementation for a hypothetical LLM application utilizing deepeval's tracing module.
from deepeval.tracing import trace, TraceType
import openai
class Chatbot:
def __init__(self):
pass
@trace(type=TraceType.LLM, name="OpenAI", model="gpt-4")
def llm(self, input):
response = openai.ChatCompletion.create(
model="gpt-4",
messages=[
{
"role": "system",
"content": "You are a helpful assistant.",
},
{"role": "user", "content": input},
],
)
return response.choices[0].message.content
@trace(type=TraceType.EMBEDDING, name="Embedding", model="text-embedding-ada-002")
def get_embedding(self, input):
response = openai.Embedding.create(
input=input,
model="text-embedding-ada-002"
)
return response['data'][0]['embedding']
@trace(type=TraceType.RETRIEVER, name="Retriever")
def retriever(self, input=input):
embedding = self.get_embedding(input)
# Replace this with an actual vector search that uses embedding
list_of_retrieved_nodes = ["Retrieval Node 1", "Retrieval Node 2"]
return list_of_retrieved_nodes
@trace(type=TraceType.TOOL, name="Search")
def search(self, input):
# Replace this with an actual function that searches the web
title_of_the_top_search_results = "Search Result: " + input
return title_of_the_top_search_results
@trace(type=TraceType.TOOL, name="Format")
def format(self, retrieval_nodes, input):
prompt = "You are a helpful assistant, based on the following information: \n"
for node in retrieval_nodes:
prompt += node + "\n"
prompt += "Generate an unbiased response for " + input + "."
return prompt
@trace(type=TraceType.AGENT, name="Chatbot")
def query(self, user_input=input):
top_result_title = self.search(user_input)
retrieval_results = self.retriever(top_result_title)
prompt = self.format(retrieval_results, top_result_title)
return self.llm(prompt)
Applying the @trace decorator will automatically log LLM traces each time chatbot.query() is called during deepeval test run. This will allow you to debug failing test cases by inspecting individual trace stacks on Confident AI.
Currently, tracing only works if you're running evaluations using deepeval test run, and generating actual_outputs from your LLM application at evaluation time (ie. tracing does not work with pre-computed outputs)
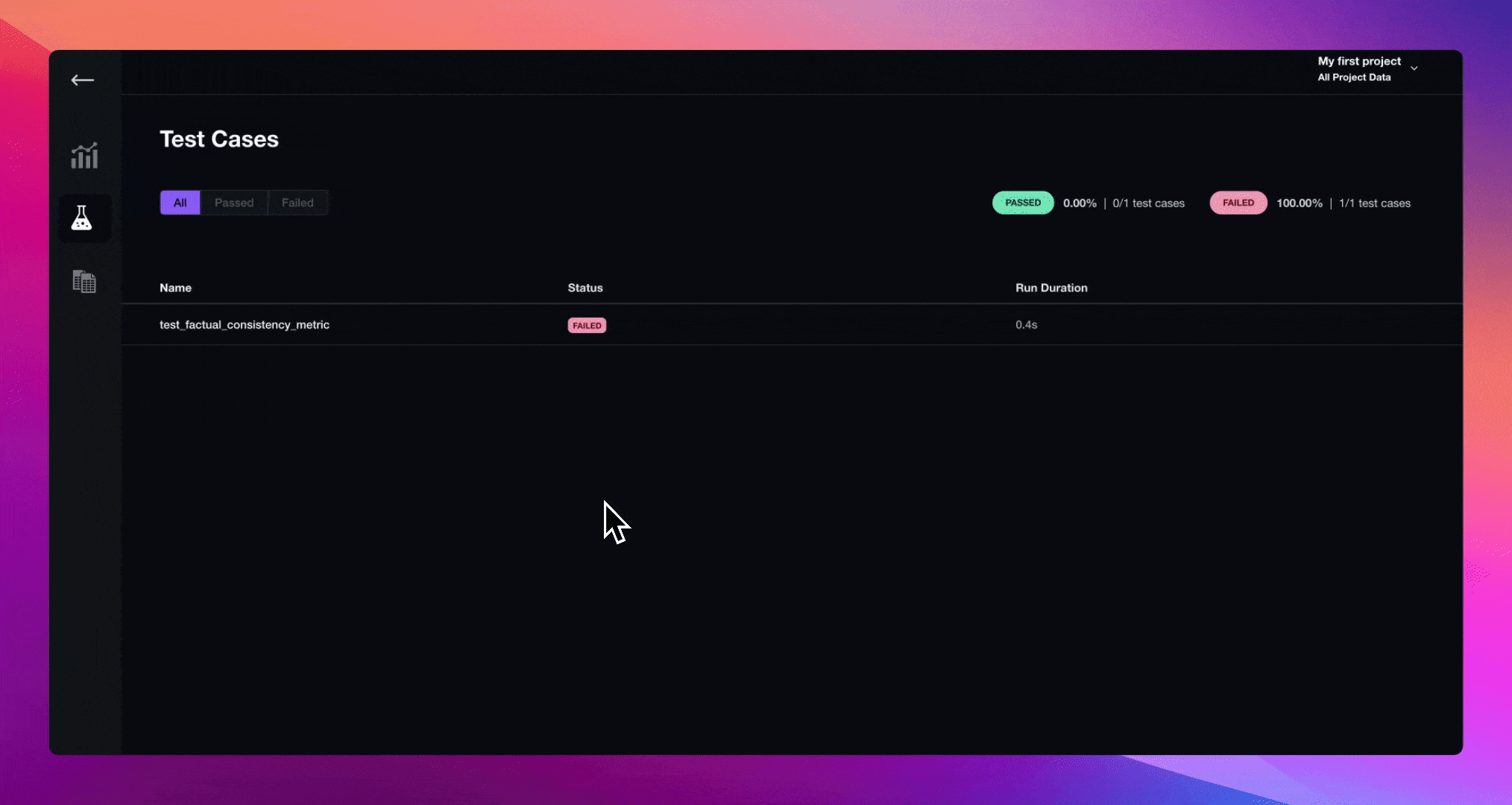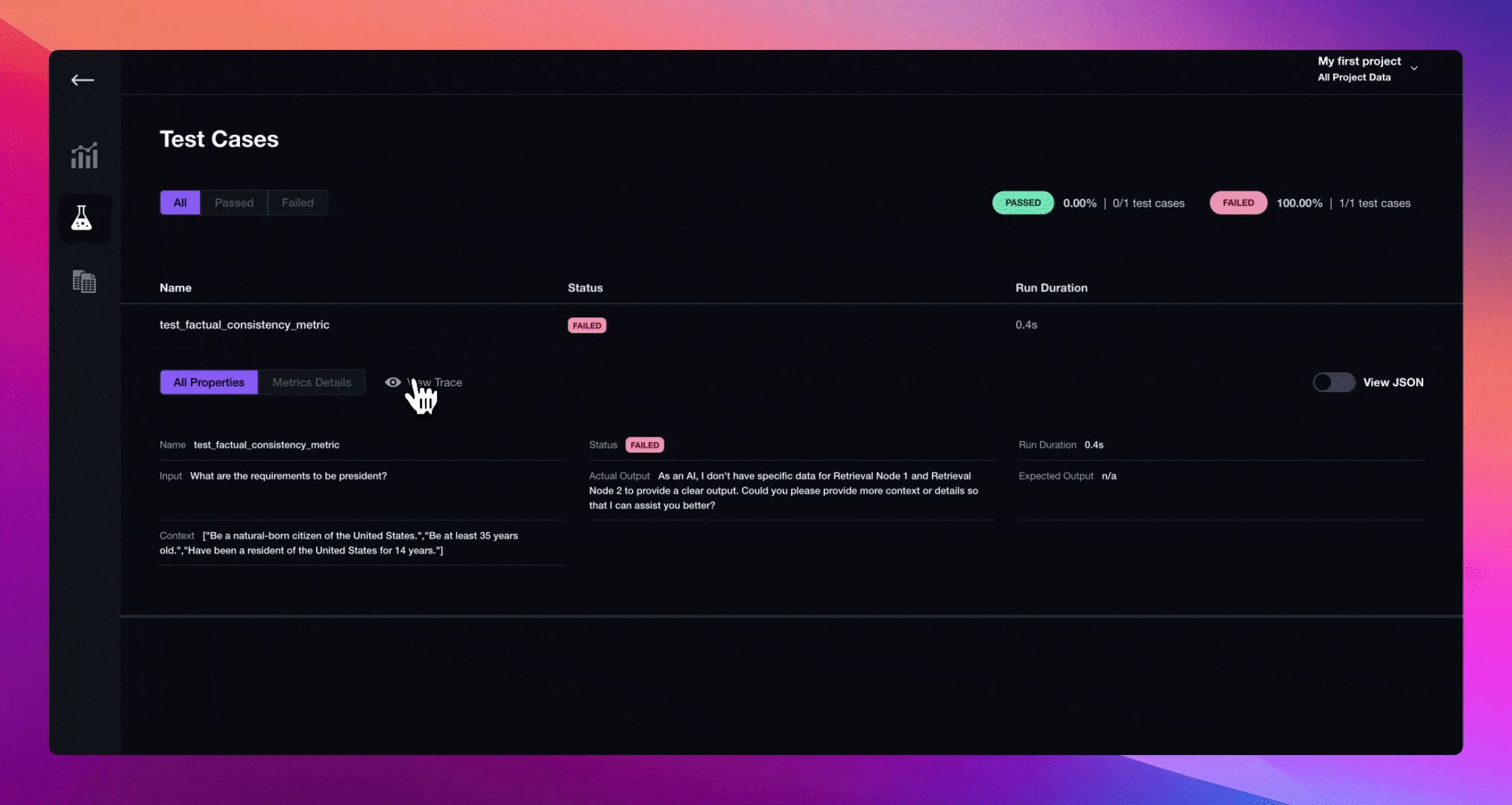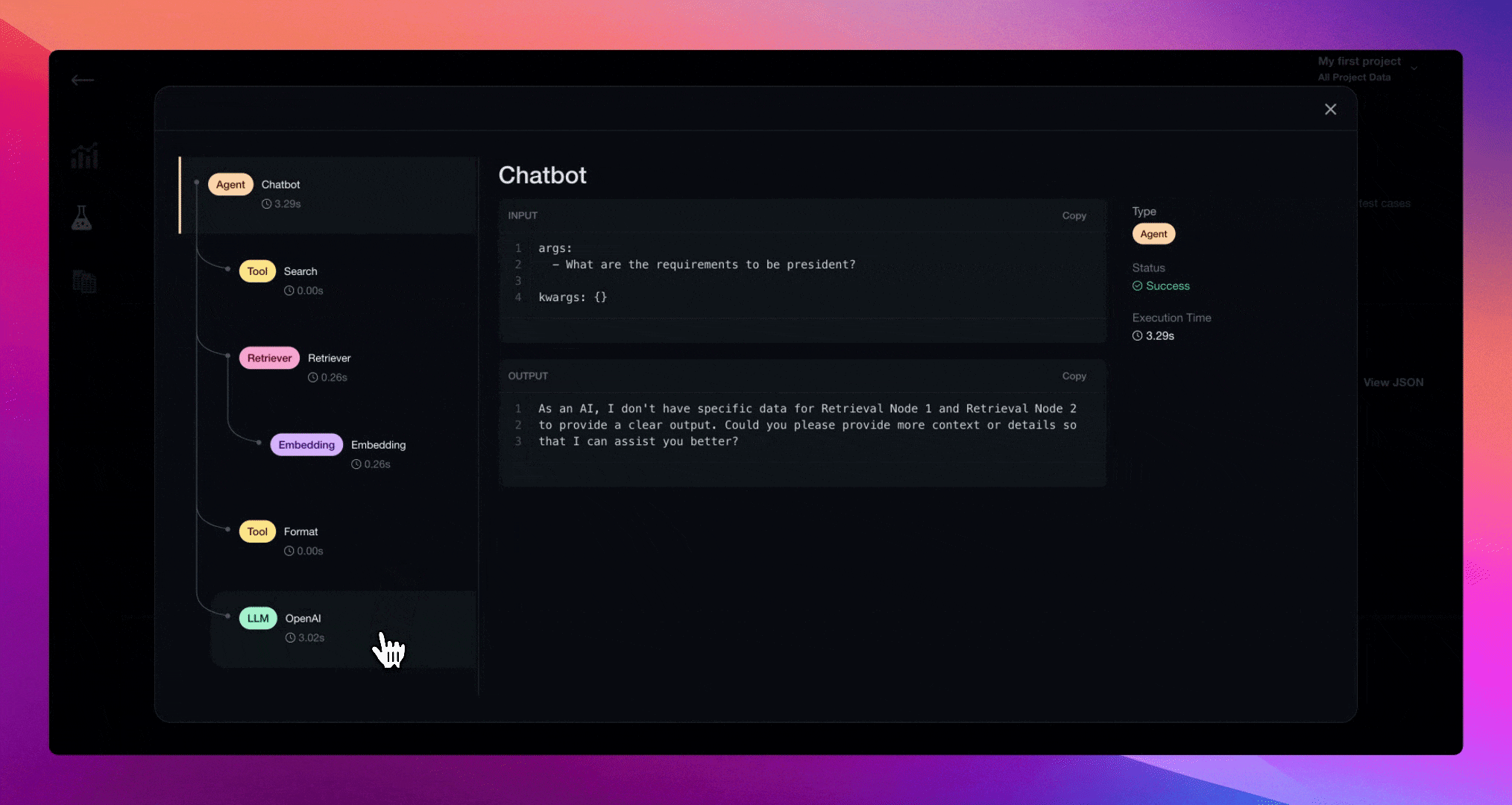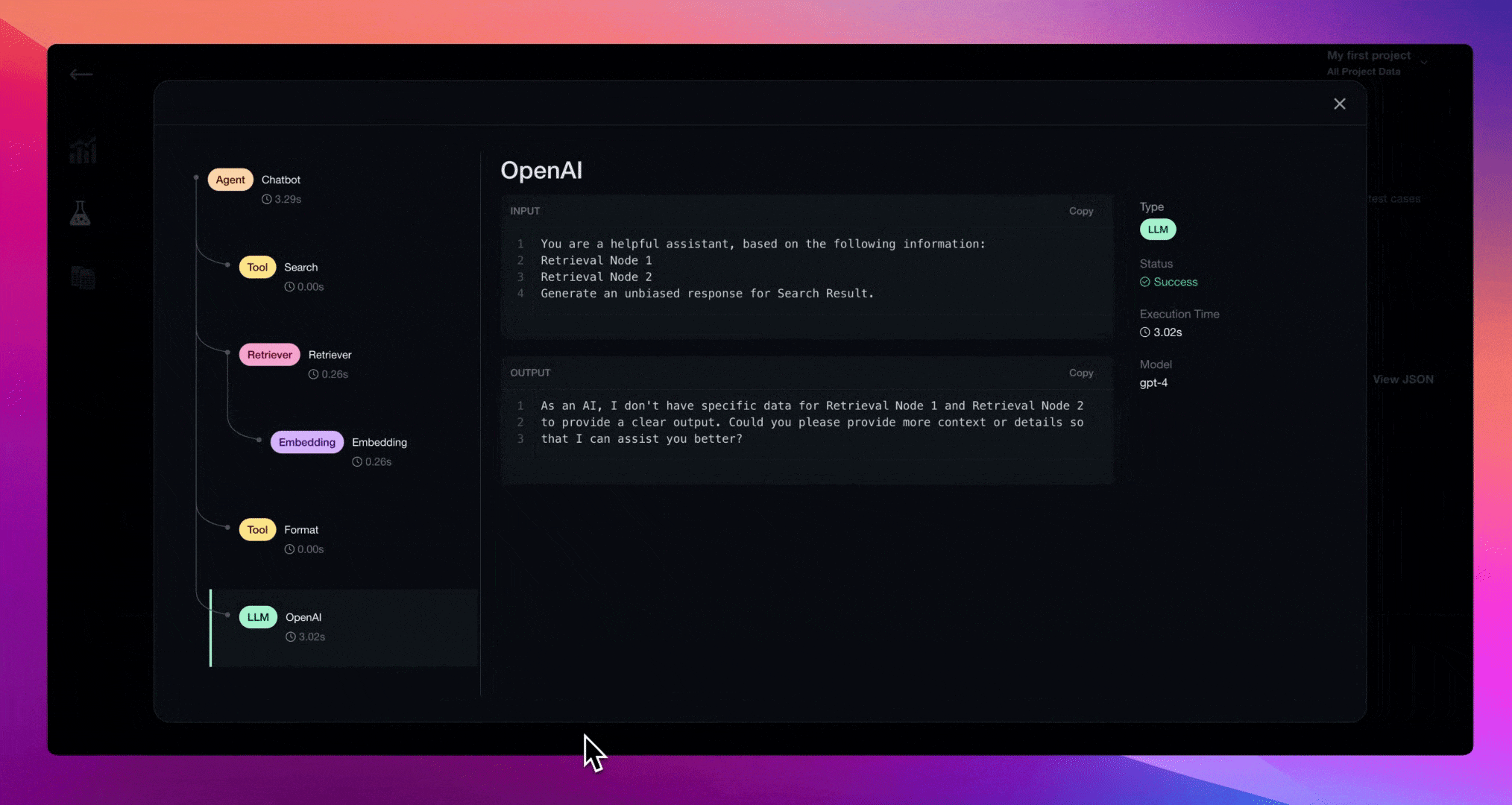
Debugging with Traces
Continuning from the previous code snippet where you've defined your Chatbot class, paste in the following test case to evaluate whether your LLM application is outputting factually correct answers.
...
import pytest
from deepeval import assert_test
from deepeval.test_case import LLMTestCase
from deepeval.metrics import HallucinationMetric
chatbot = Chatbot()
def test_hallucination():
context = [
"Be a natural-born citizen of the United States.",
"Be at least 35 years old.",
"Have been a resident of the United States for 14 years."
]
input = "What are the requimrents to be president?"
metric = HallucinationMetric(threshold=0.8)
test_case = LLMTestCase(
input=input,
actual_output=chatbot.query(user_input=input),
context=context,
)
assert_test(test_case, [metric])
Lastly, run deepeval test run:
deepeval test run test_chatbot.py
You can now go to Confident AI to debug failing test cases with tracing.
Full Example
You can find the full example here on our Github.